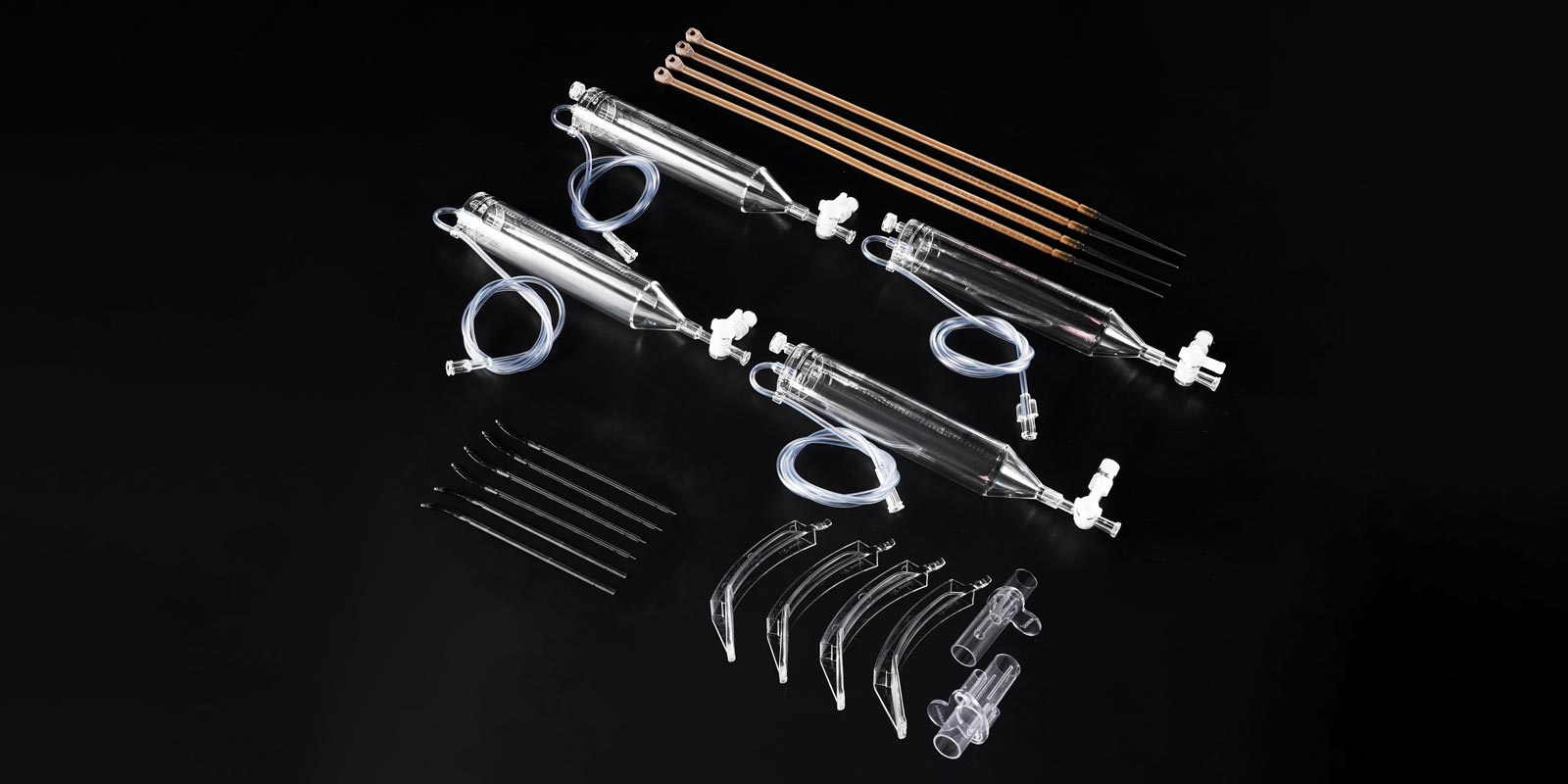
In the field of medical mold design and manufacturing, motorized lateral core-pulling mechanisms play a crucial role, directly affecting the molding quality, production efficiency, and service life of molds. Below is a detailed introduction to the classification and characteristics of several common motorized lateral core-pulling mechanisms in medical molds.
1. Angle Pin Core-Pulling Mechanism
The angle pin core-pulling mechanism is widely used in medical molds and has significant characteristics.
-
Power Source: This mechanism uses the mold-opening force of the injection molding machine as the pulling force, cleverly utilizing the existing power of the machine and eliminating the need for additional complex power devices, thus simplifying the overall mold structure.
-
Structural Advantage: Its simple structure makes it commonly used for core-pulling of small and medium-sized cores. This simple structure not only reduces the manufacturing cost of the mold but also facilitates installation, debugging, and maintenance.
-
Applicable Scenarios: It is mainly used to pull out cores that are close to the parting surface and have relatively small pulling forces. In medical molds, the forming of some small and relatively simple-structured parts often uses this mechanism.
-
Mold-Opening Distance: A relatively large mold-opening distance is required for core-pulling, which necessitates that the injection molding machine has sufficient mold-opening stroke to ensure the smooth completion of the core-pulling action.
-
Pulling Direction: The pulling direction generally needs to be parallel to the parting surface. This design makes the core-pulling process more stable and reduces the risk of part damage due to directional deviation.
-
Delayed Core-Pulling: The delayed core-pulling distance is relatively short, which can meet the usage requirements in some occasions where the timing of core-pulling is not critical.
2. Cam Core-Pulling Mechanism
The cam core-pulling mechanism has unique advantages in specific situations.
-
Applicable Cores: It is used to pull out cores that are far away from the parting surface in the vertical direction. In medical molds, when parts have special structures that require pulling out cores far from the parting surface, the cam core-pulling mechanism is a good choice.
-
Load-Bearing Capacity: Compared with angle pins, cams with the same cross-section can withstand larger pulling forces. This makes the cam core-pulling mechanism more advantageous in situations where higher pulling forces are required, ensuring the reliability and stability of the core-pulling process.
-
Delayed Core-Pulling: The delayed core-pulling distance is large, which can meet the process requirements for long-time delayed core-pulling and provides more flexibility for mold design.
-
Structural Layout: The cam can be placed outside the mold. This layout makes the mold structure more compact, reduces the space occupied by the mold, and helps improve production efficiency.

3. Inclined Slider Core-Pulling Mechanism
The inclined slider core-pulling mechanism has a unique working mode and applicable characteristics.
-
Applicable Surfaces: It is suitable for pulling out convex and concave surfaces with shallow forming depths and large areas on the sides. In medical molds, the forming of some parts with complex side shapes often uses this mechanism to accurately pull out the required cores.
-
Simultaneous Actions: Core-pulling and ejection actions are completed simultaneously. This synchronous action design improves the production efficiency of the mold and reduces the production cycle.
-
Special Advantages: The parting surface of the inclined slider is conducive to improving overflow and venting conditions. During the injection molding process, good overflow and venting can reduce defects such as bubbles and shrinkage in the parts, improving part quality.
-
Locking Method: The inclined slider is locked by a mold sleeve, and the locking force is related to the mold clamping force. This locking method ensures the stability of the inclined slider during the injection molding process and prevents displacement and deformation of the core.
4. Rack and Pinion Core-Pulling Mechanism
The rack and pinion core-pulling mechanism has some unique functions and limitations.
-
Angle Applicability: It can pull out cores at any angle to the parting surface and with relatively small pulling forces. In medical molds, when parts have complex angular requirements, this mechanism can meet different core-pulling needs.
-
Core-Pulling Stroke: The core-pulling stroke is equal to the core-pulling distance, allowing it to pull out longer cores. This gives it an advantage in situations where longer cores need to be pulled out.
-
Delayed Core-Pulling: It can achieve long-distance delayed core-pulling for cores in different directions, providing more possibilities for mold design and meeting some special process requirements.
-
Structural Characteristics: However, the mold structure of this mechanism is complex, the manufacturing cost is high, and it requires high precision in mold machining and assembly.
Dongguan Yize Mould Co., Ltd. was founded in 2007 and is headquartered in Dongguan, the manufacturing capital of China, with convenient transportation and logistics. Relying on the local advantageous conditions, the company has been focusing on precision mold design and manufacturing as well as precision injection molding product production for many years. The company integrates product design, precision mold manufacturing, injection molding and assembly, and after-sales service for automotive connectors, medical product injection molding, cleanroom injection molding, and PFA custom injection molding, providing customers with complete solutions. If you have relevant needs, please feel free to contact us at +86 13302615729 (WeChat and Whatsapp available).














 Home
Home
