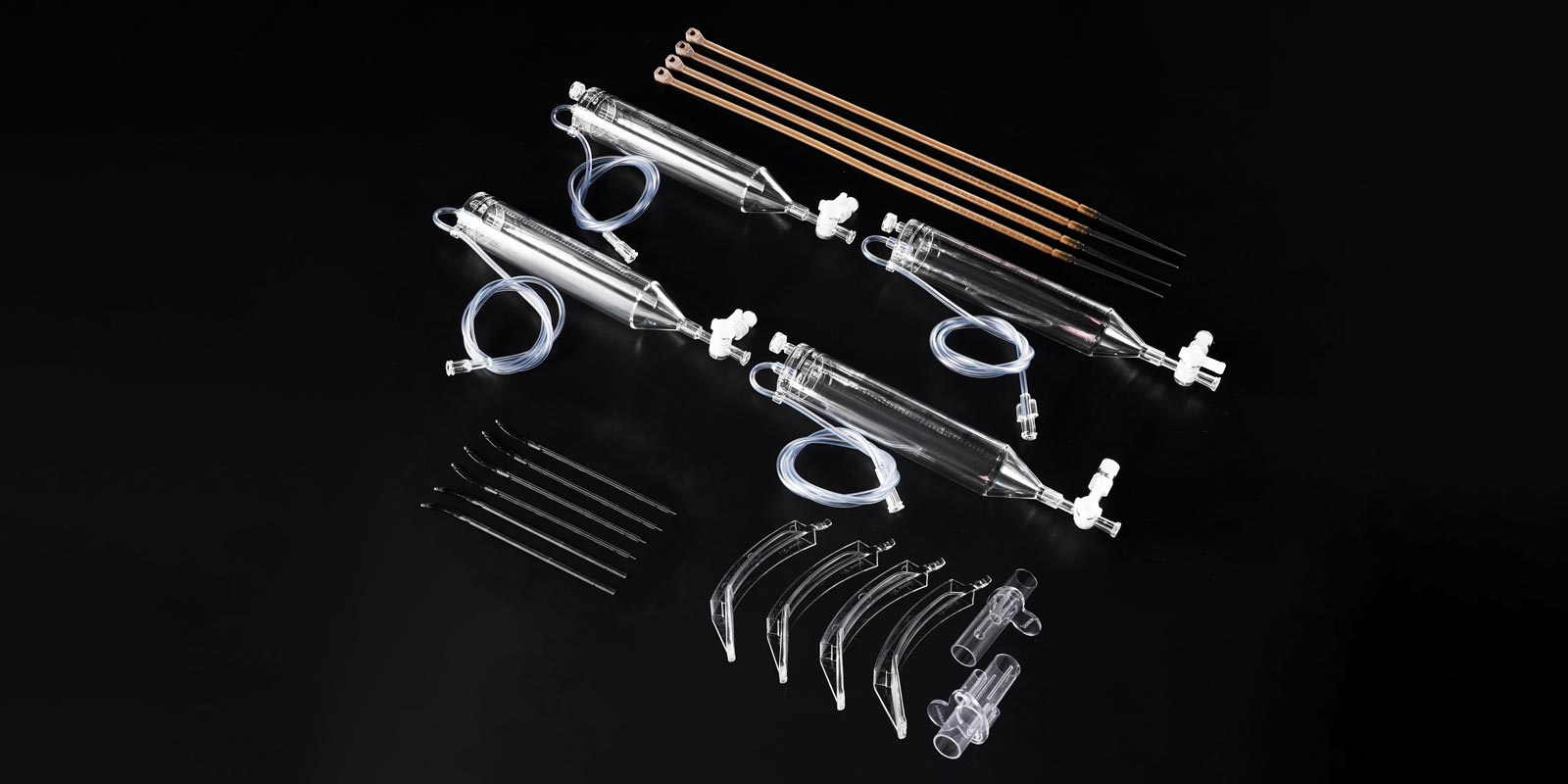
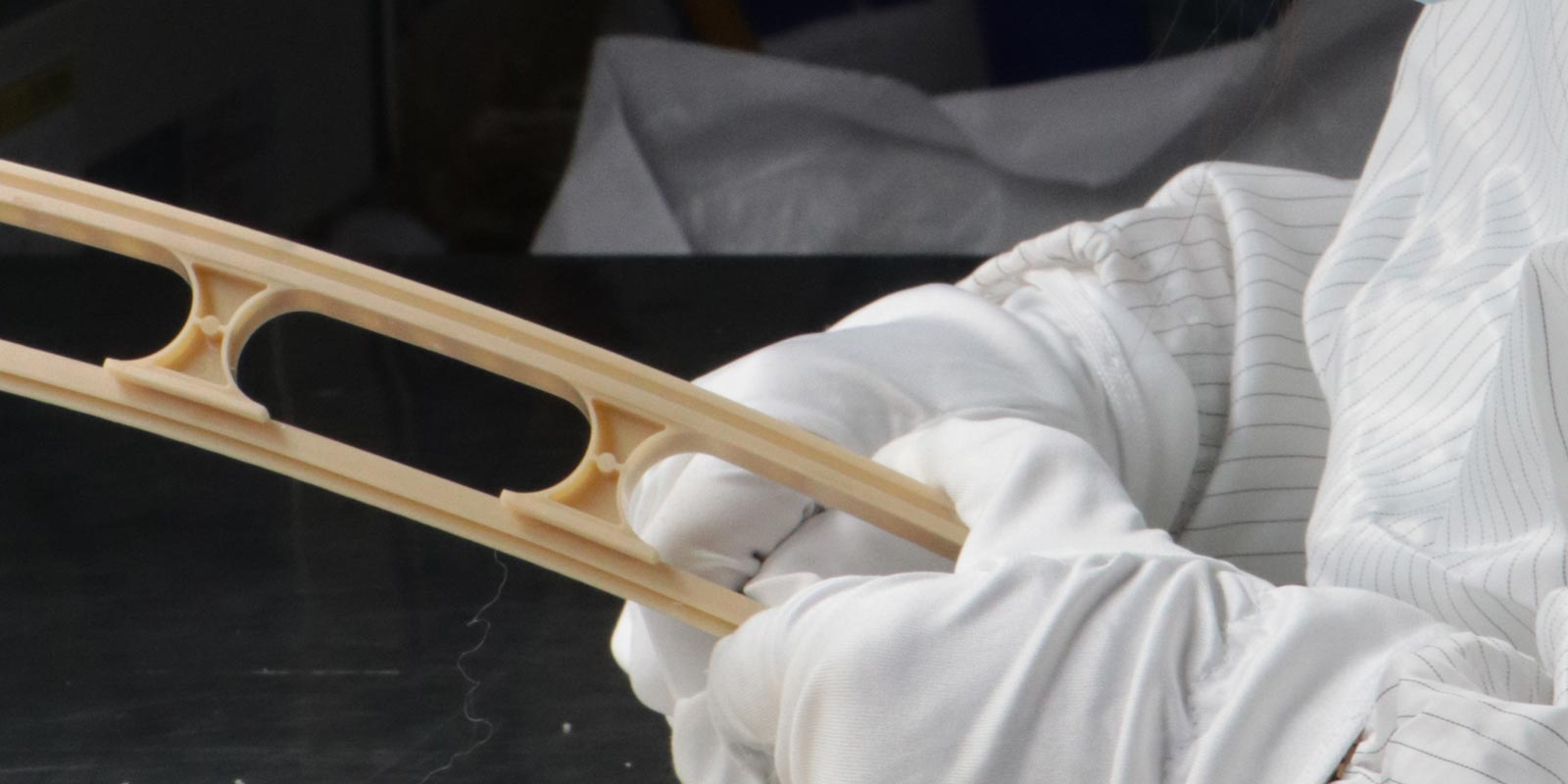
In the realm of medical injection molding, precise control of the molding process is crucial to ensuring product strength. Dongguan Yize Mould, a seasoned professional in the field, delves into the core process parameters that directly impact the strength of injection molded parts.
1. Injection Pressure: The Key to Enhancing PP Part Strength
Polypropylene (PP) stands out among plastics for its excellent elasticity. Increasing injection pressure significantly enhances the density of injection molded parts, subsequently boosting their tensile strength. This effect is particularly pronounced in PP materials. However, once density reaches the material's limit, further pressure increases do not enhance tensile strength but instead lead to internal stress accumulation, making the parts brittle. Thus, fine-tuning injection pressure to find the balance between strength and ductility is key to improving PP part quality.

2. Hot Oil Injection: The Secret to Optimizing the Performance of Nylon and POM Parts
For crystalline plastics like nylon and polyoxymethylene (POM), hot oil injection molding markedly improves product impact resistance and tensile strength. By slowing down the cooling rate, it not only promotes thorough crystallization but also reduces residual internal stress. Notably, hot oil-injected parts may differ in size from those produced via traditional water-cooled injection, with nylon parts potentially being slightly larger, a factor to consider during design.
3. Melt Speed: A Double-Edged Sword in PVC Injection Molding
In the injection molding of PVC, especially 90-degree grade material, 180°C is generally considered an appropriate processing temperature. However, excessively fast melt speeds, even at this temperature, can lead to under-curing. Rapid screw retraction reduces the time for material heating and mixing, resulting in uneven melting and significantly compromising the strength and toughness of the molded parts. Therefore, operators should avoid setting the melt rotation speed above 100 rpm without caution. If higher speeds are necessary, corresponding increases in material temperature by 5-10°C or adjustments to melt backpressure are recommended, along with regular checks to prevent under-curing-related quality losses.














 Home
Home
