Inserts are widely used in the processing of medical injection moulds, primarily in the front mold, rear mold, sliders, and lifters. So, what is the reason behind the preference for inserts in medical injection molding die processing, and what purposes do they serve? Let's delve into it together.
-
Wise Choice of Inserts for Material Savings
Injection molds are known to use regular, shaped blocks of steel to secure materials. However, the height of the front and rear molds is determined by the z-axis dimension. Whether it's the front or rear mold, if a certain area protrudes higher than others, inserts can be made to reduce the overall height of the mold.
-
Flexible Mold Modification with Inserts
Medical molds often require frequent modifications. By designing easily modifiable parts as inserts, only the inserts need to be replaced during mold changes. Additionally, multiple inserts can be prepared during the mold opening stage for future replacements, facilitating easy modifications to the mold.
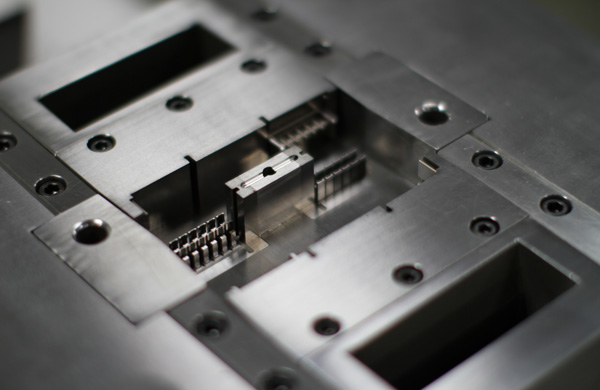
-
Optimized Venting with Inserts
Venting is crucial in medical injection molding. Poor venting can lead to trapped air in the mold cavity, especially in deeper sections. During injection molding, this can result in defects such as bubbles, shrinkage, incomplete filling, whitening, or black spots. Therefore, inserts can be added where venting is needed, utilizing the gap between the inserts for effective venting.
-
Processing Convenience with Inserts
Some deep sections in injection molds are difficult to machine with traditional tools. Although electrical discharge machining (EDM) can be used, it is slow and inefficient. Therefore, inserts are often chosen to reduce machining difficulty and facilitate venting. Additionally, for deep sections that require polishing, it is much more convenient to disassemble and polish the inserts.
-
Extended Mold Life with Inserts
Typically, areas in medical injection molds that require inserts are often the most prone to damage. Once an insert is damaged, it can be easily replaced, thereby extending the life of the injection mold and saving time and money.














 Home
Home
