The production of medical injection molds is an extremely complex and precise engineering project, encompassing multiple key links. Each link plays a crucial role in determining the quality and performance of the final mold. Below is a detailed introduction to the production process flow of medical injection molds.
I. Material Preparation: Laying the Foundation for Quality
In mold manufacturing, steel is often the preferred material due to its excellent mechanical properties and wear resistance. During the material preparation stage, the primary task is to carefully select the appropriate type of steel and conduct rigorous material testing and analysis to ensure that the material quality meets the established requirements. Subsequently, methods such as sawing or shearing are used to precisely cut the steel to the required dimensions according to the specifications of the mold design drawing.
Taking S136 and 718 steels as examples, there are significant differences between the two in terms of nature, hardness, performance, application scenarios, and price. 718H mold steel is a pre - hardened mirror - finish acid - resistant mold steel with a factory hardness of HRC32 - 36. It has good electrical and grain - processing properties, and there is no risk of quenching cracks or heat - treatment deformation. It is mainly used for large - scale, long - life plastic injection molds, such as those for household appliances. S136 mold steel, on the other hand, is a corrosion - resistant and rust - proof mirror - polished mold steel that requires quenching and hardening, with a quenching hardness of HRC48 - 52. Although it needs heat treatment, it has little deformation and good permeability. The surface can still maintain its original smoothness after long - term use, and it can be stored in humid environments without special protection. It is commonly used for high - mirror - finish plastic products, such as optical mirror - finish plastic products or injection molds requiring corrosion - resistant and rust - proof functions, as well as precision medical molds. The price of 718H mold steel does not exceed 40 yuan per kilogram, while the price of S136 mold steel varies greatly, ranging from more than 20 to more than 100 yuan per kilogram.
II. Mold Design: Outlining the Precise Blueprint
Mold design is the core step in the entire production process, directly affecting the manufacturing quality and performance of the mold. In this stage, designers need to carefully design the mold structure according to the specific requirements of customers and product - related requirements, covering aspects such as the shape, size, and layout of mold components. Every detail needs to be repeatedly considered to ensure the rationality and feasibility of the design.
After the design is completed, advanced CAD software is used to build a three - dimensional model, which can visually display the structure and working principle of the mold through virtual simulation technology. At the same time, mold flow analysis and precise calculation of mold strength are carried out to simulate the flow of plastic during the injection molding process and analyze the strength and stability of the mold under stress, fully ensuring the reliability and rationality of the design.
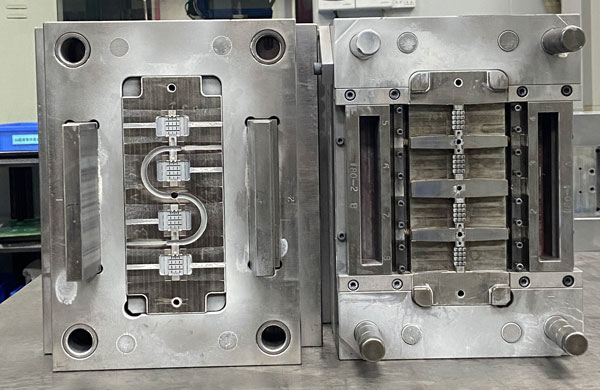
III. Manufacturing: Sculpting Precision Components
The manufacturing process is the core battlefield of mold production, encompassing a series of processes such as rough machining, heat treatment, machining, and finish machining.
Rough machining is like the initial carving of a sculptor, reducing the initial size of the raw material to an appropriate range to prepare for subsequent fine machining. The next step is heat treatment, which is a key step in improving the performance of the mold. Through processes such as quenching and tempering, the internal structure and properties of the material are changed, significantly improving the hardness and wear resistance of the mold so that it can withstand the high temperature and pressure during the injection molding process.
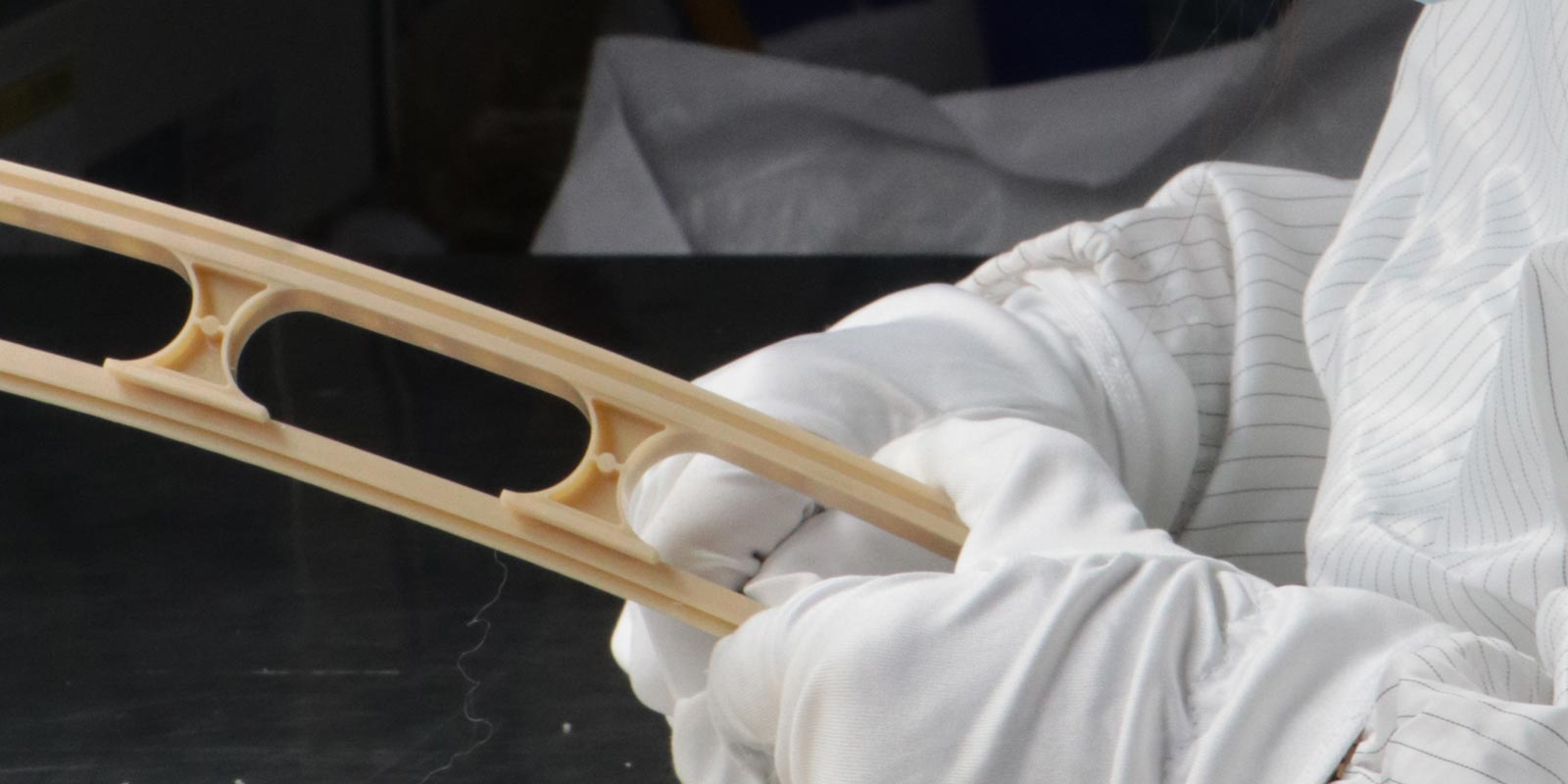
Then comes the machining process, which is one of the most delicate steps in the entire manufacturing process. Workers strictly follow the mold design drawing to perform various machining operations such as turning, milling, grinding, and drilling. Each movement is precise, like creating art in the micro - world. Finally, finish machining is carried out, using processes such as scraping and lapping to trim the surface of the mold, improving the machining accuracy of the mold to the extreme and ensuring that all parts of the mold can fit perfectly.
IV. Debugging and Trial Molding: Testing and Optimizing Performance
The debugging and trial - molding stage plays a crucial role in connecting the preceding and following processes in mold production. By debugging and trial - molding the mold, its performance and accuracy can be comprehensively tested and optimized.
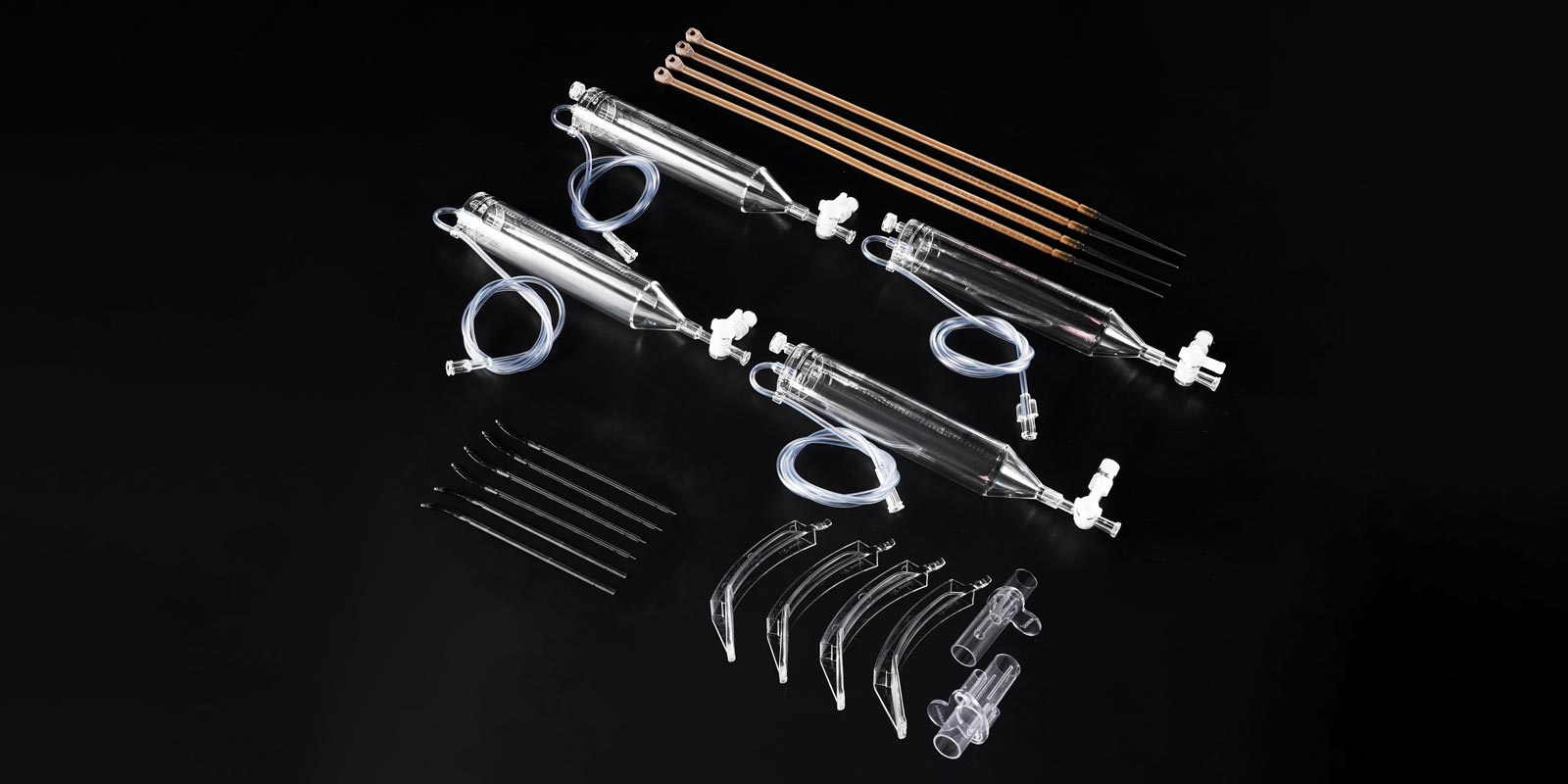
First, the mold needs to be installed and adjusted to ensure that the fit between all mold components is precise and the working state is normal. This is like assembling a precision instrument, where each part must be installed in place to ensure the normal operation of the instrument. Then, the trial - molding operation is carried out, using the mold to produce samples or products, and adjustments and improvements are made according to the actual situation. During this process, close attention needs to be paid to issues such as the molding quality, dimensional accuracy, and surface finish of the products, striving to meet the expected requirements of the products and the diverse needs of customers.
V. Mold Maintenance: Extending Service Life
Mold maintenance, as the final step of the production process, is of great significance for extending the service life of the mold and improving production efficiency. This is like performing regular maintenance on a car to ensure that it always remains in good running condition.
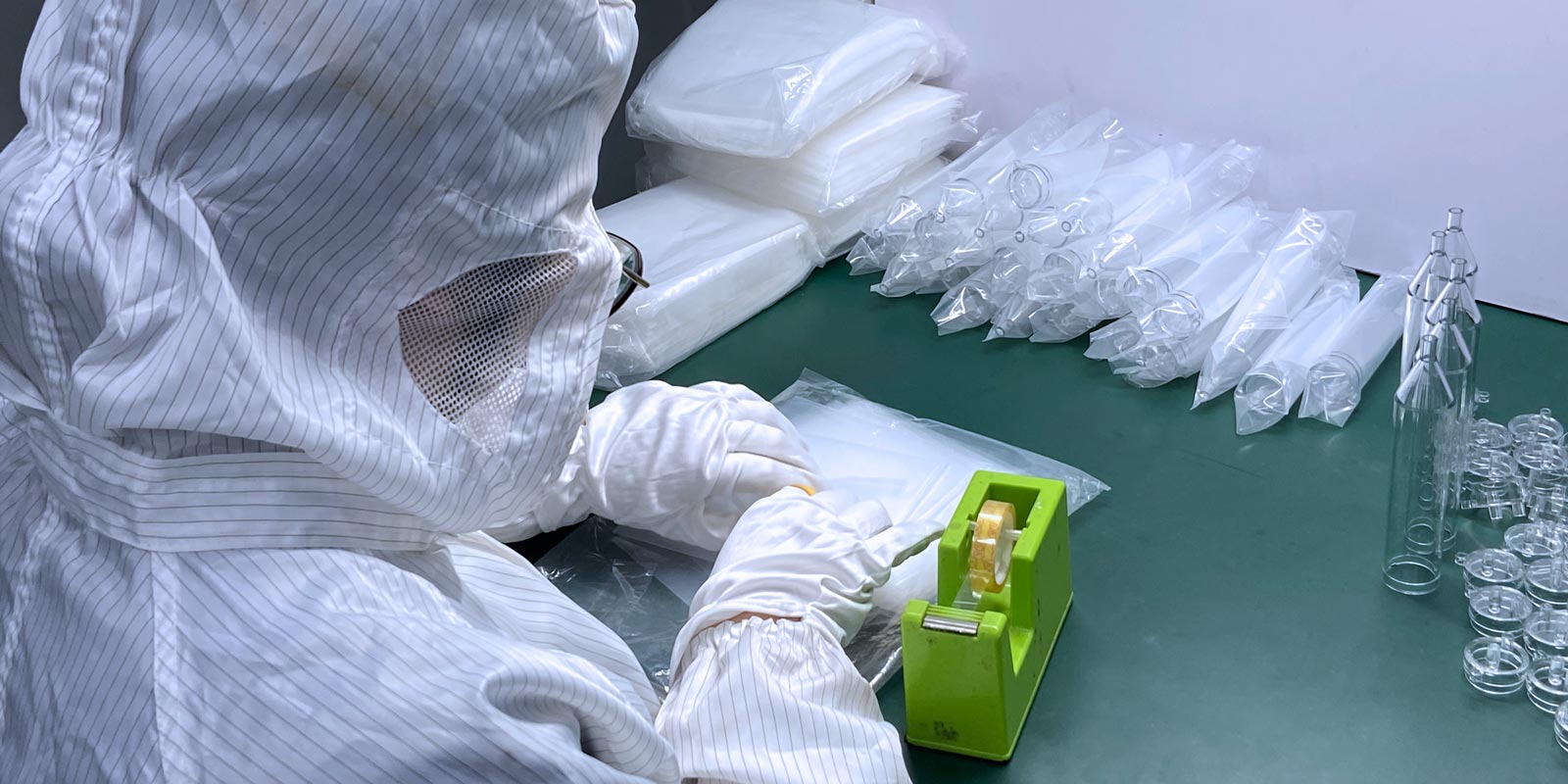
Regular maintenance work needs to be carried out, including cleaning, lubrication, rust - proof treatment of the mold, and replacement of worn - out parts. Regular cleaning of the mold can remove dirt and impurities on the surface and prevent them from corroding the mold; proper lubrication can reduce friction between mold components and reduce wear; rust - proof treatment can prevent the mold from rusting in humid environments; and timely replacement of worn - out parts can ensure that the performance of the mold is always at its best. At the same time, good record - keeping and account management of the mold should be done, detailedly recording the usage, maintenance history and other information of the mold, so as to accurately count and deeply analyze the usage status of the mold and effectively improve the management level of the mold.
In summary, the production process flow of medical injection molds consists of five major links: material preparation, mold design, manufacturing, debugging and trial molding, and mold maintenance. These links are closely connected and complement each other, forming an organic whole. Only by following a scientific and standardized process flow can high - quality molds that meet customer requirements be manufactured. Therefore, finding a good medical injection mold manufacturer is crucial. Due to the many production processes involved in medical injection molds, the mold processing cycle of medical injection mold factories is relatively long, usually around 30 - 35 days, depending on the actual product structure. If you have mold - making needs, you can contact us at Yize Mould in advance, and we will provide you with a professional custom - made solution for medical injection molds.














 Home
Home
