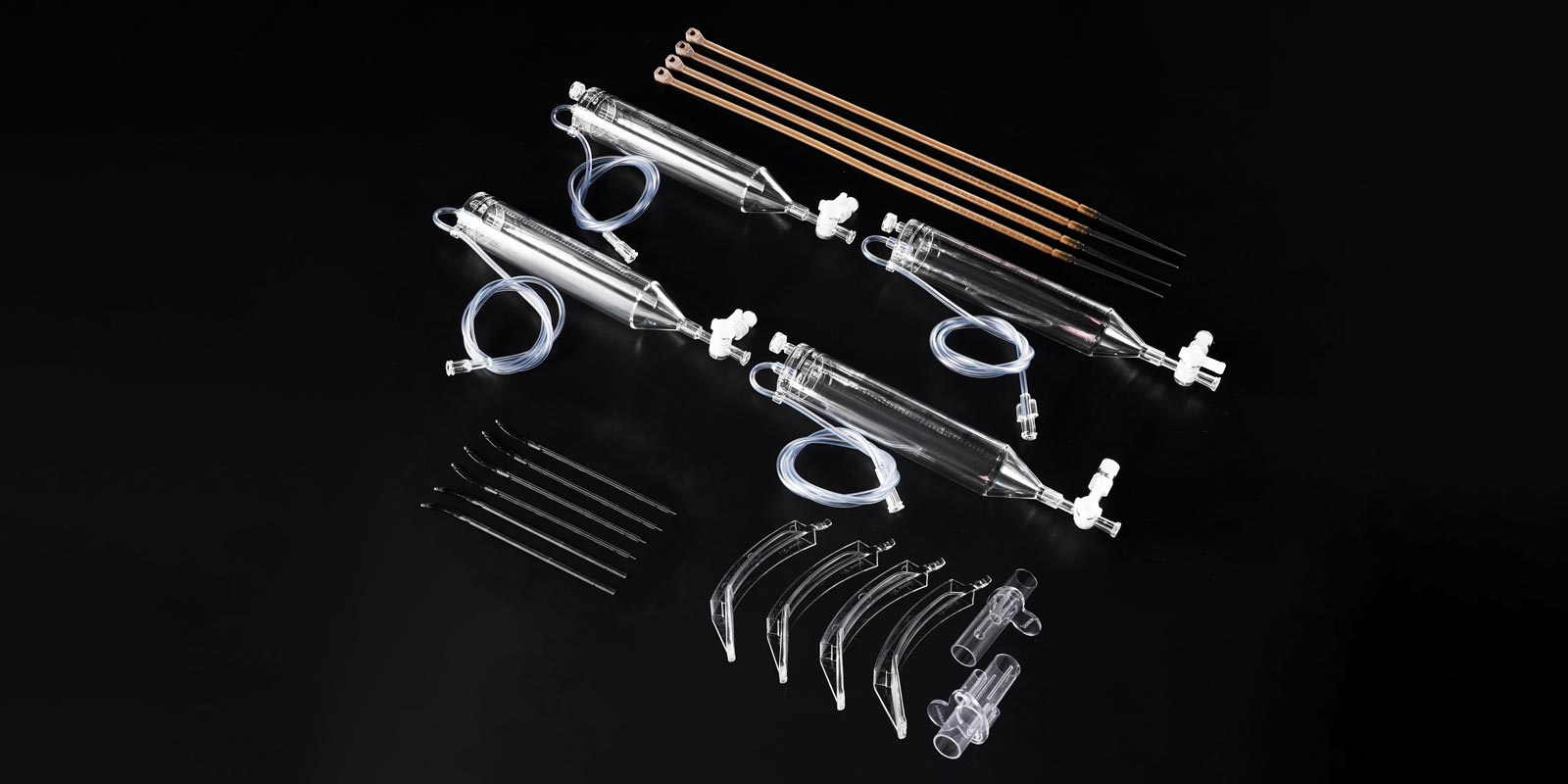
High-temperature plastic injection molding technology for medical device components aims to meet the stringent requirements of engineering fields such as medical devices, medical equipment, and medical consumables for plastic materials with high mechanical properties and chemical resistance in high-temperature working environments. However, the application of high-temperature plastics in medical devices is not solely due to their high-temperature resistance but also because of their lightweight, self-lubricating, and wear-resistant properties. Especially in medical consumables that require high-temperature or steam sterilization, the selection of high-temperature plastics such as PPSU, LCP, and PES becomes particularly important.
Compared to ordinary PP and nylon, their mechanical working conditions are generally limited to below 100℃, while the general working temperature of PC is also below 140℃. It is worth noting that there are differences in temperature resistance among plastic materials from different manufacturers, especially for some modified ordinary plastics, where the gap in temperature resistance with raw materials is more pronounced.

High-temperature engineering injection molding plastics, due to their special structure, can maintain high mechanical properties in high-temperature working environments. These plastics often require high-temperature injection molding during the production process, which poses higher temperature requirements for the heating system of the injection molding machine. However, the default barrel temperature of most injection molding machines is below 350℃, which places higher demands on the selection of high-temperature plastics and the injection molding process.
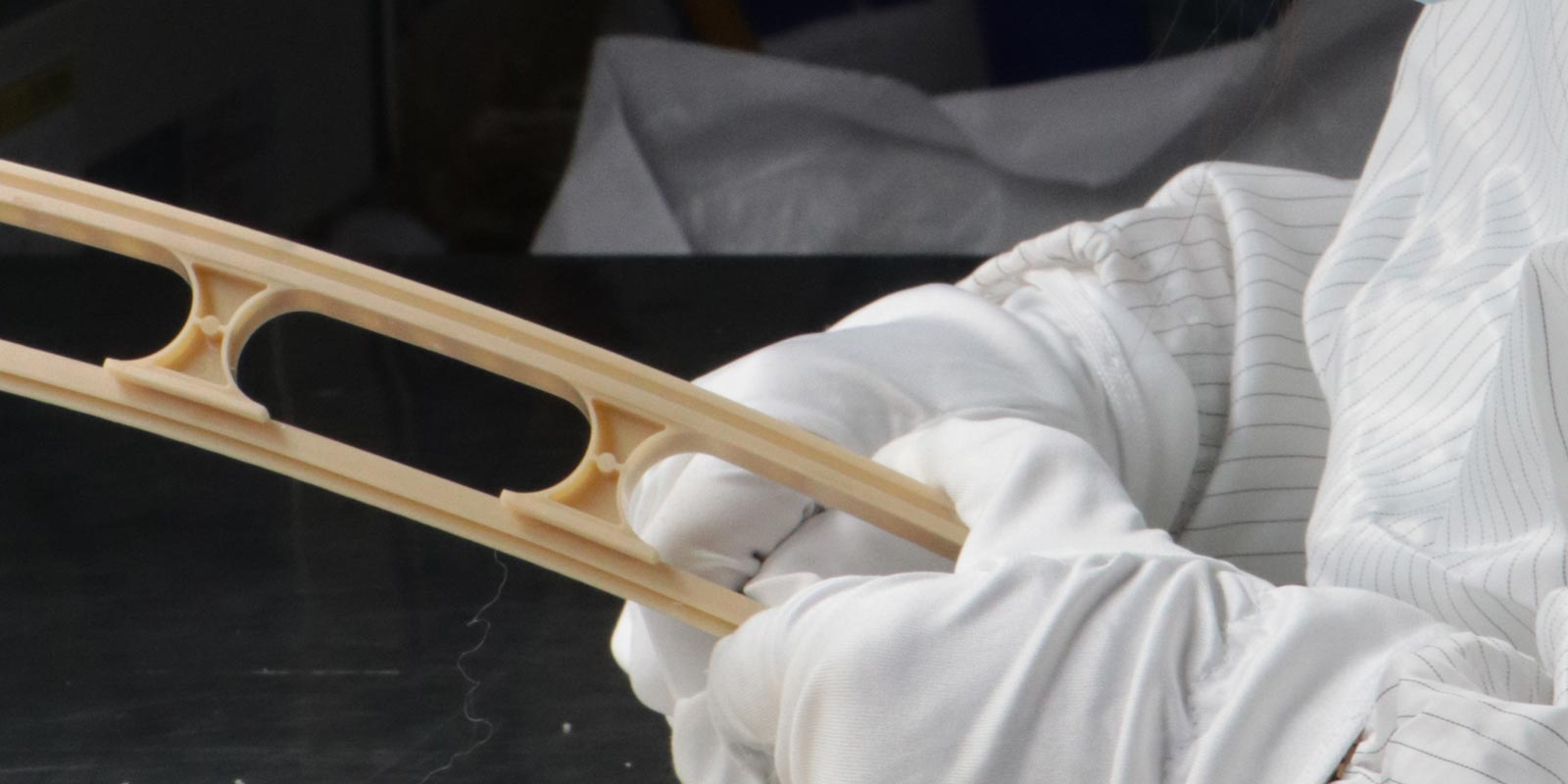
Here, we briefly introduce medical-grade LCP plastic. LCP combines the structural design of wholly aromatic polyesters and copolyesters, and it also possesses a delicate linear polymer chain structure design, which enables its products to have good unidirectional mechanical properties. LCP exhibits excellent high-temperature performance (heat deflection temperature of 121-355℃) and also possesses good radiation resistance, hydrolysis resistance, weather resistance, chemical resistance, flame retardancy, low smoke generation, high stability, low moisture absorption, extremely low linear expansion coefficient, high impact strength, and rigidity (LCP is stronger than steel at the same weight but has only 15% of steel's rigidity). LCP can withstand chemicals such as acids, solvents, and hydrocarbons and has good barrier properties. In the medical industry, LCP has a wide range of applications. For example, fixed compression plate LCP is a new type of fracture internal fixation technology developed based on dynamic compression plates and point contact plates. Medical-grade LCP plastic offers advantages such as high fixation reliability, low nail extraction rates, and fewer complications, resulting in strong surgical outcomes. Its internal fixation allows for early functional training, can shorten the recovery period after injury for patients, and fully exerts joint function.














 Home
Home
