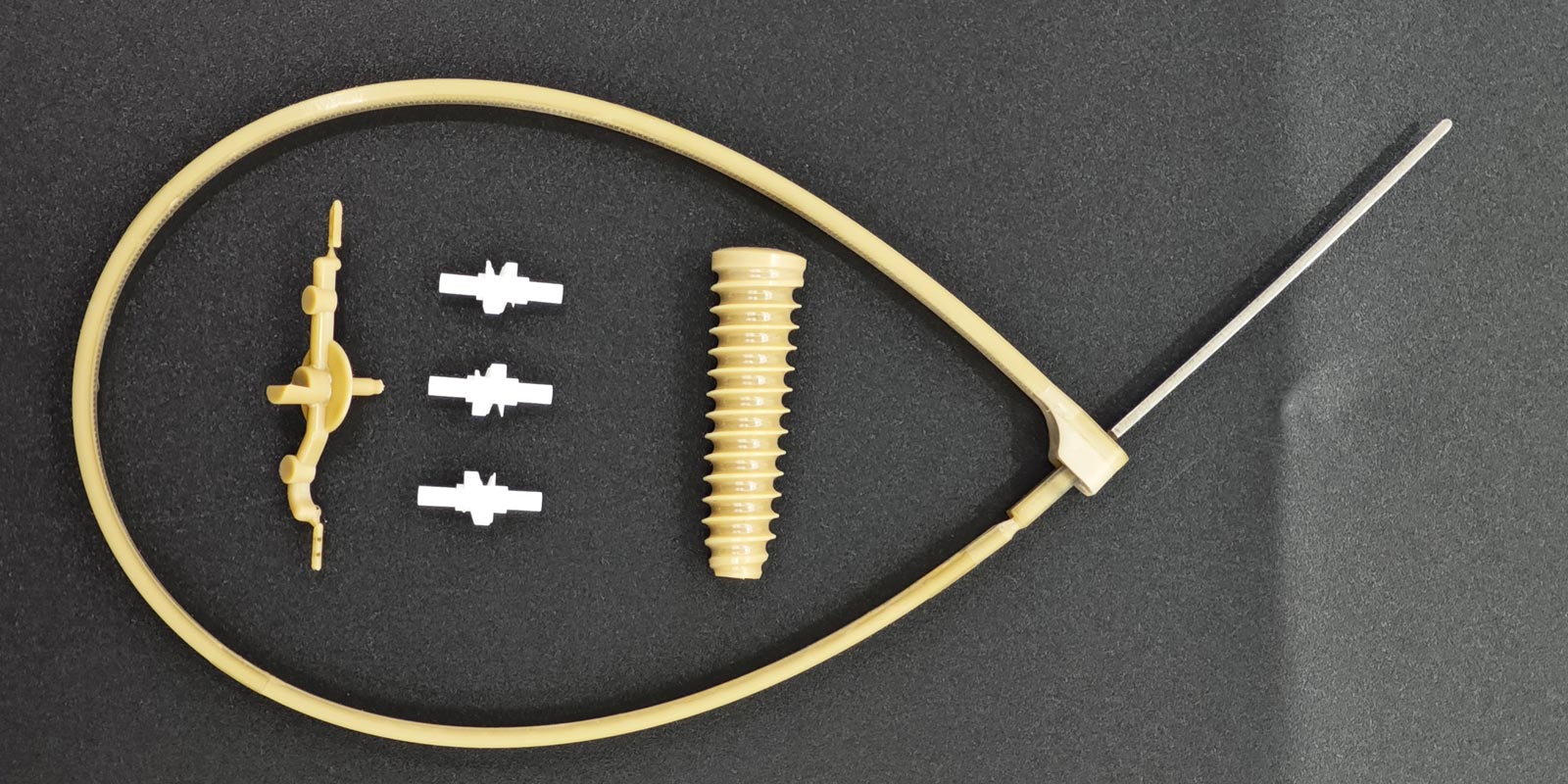
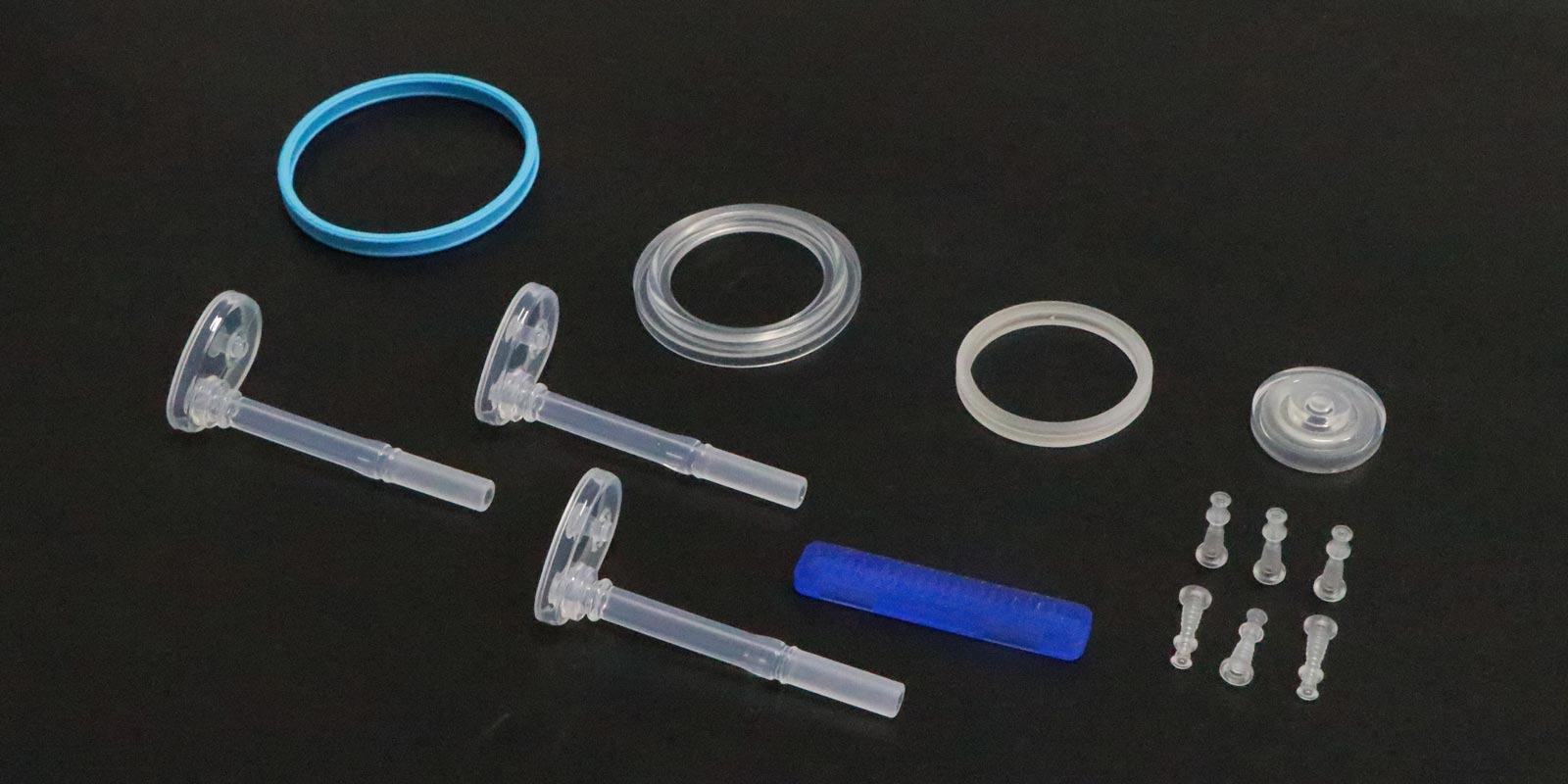
Medical injection molding, as the core process in medical device manufacturing, achieves high-precision, mass production of components by injecting medical-grade plastics into precision molds under high temperature and pressure. The process encompasses four key stages: raw material processing, mold design, injection molding, and quality inspection, each of which must meet the stringent requirements of the medical industry for biocompatibility, cleanliness, and functionality.
I. Raw Material Preparation: Dual Screening for Biocompatibility and Sterilization Resistance
The selection of raw materials for medical injection molding is the first line of defense for product safety. Commonly used materials include:
-
Polycarbonate (PC): Used in syringes and IV connectors, offering both transparency and impact resistance.
-
Polyetheretherketone (PEEK): Employed in orthopedic implants, withstanding high temperatures and matching the strength of metals.
-
Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR): Utilized in catheters and seals, providing a soft touch and chemical stability.
-
Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE): Applied in surgical instrument handles, achieving rubber-like flexibility and fatigue resistance.
Key Control Points:
-
Supplier Qualification Verification: Suppliers must hold ISO 10993 biocompatibility certification and provide FDA 510(k) or NMPA registration documents.
-
Batch Testing: Each batch of raw materials must undergo testing for molecular weight distribution (fluctuation ≤5%) and metal impurity particle size (<10 μm).
-
Pre-processing: Raw materials should be stored in a constant-temperature warehouse at 20 ± 2°C and used within 8 hours of unpacking. They must also be dried to remove moisture (dew point ≤ -40°C).
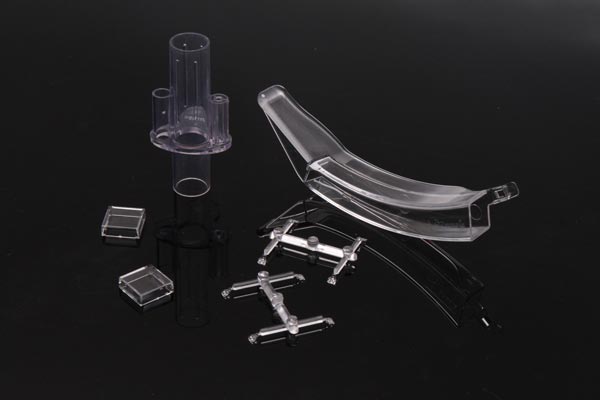
II. Mold Design: The Art of Micron-Level Precision and Functional Integration
The design of medical molds must balance structural complexity with production stability. Typical examples include:
-
Cardiac Stent Catheter Molds: The runner length-to-wall thickness ratio is controlled at 80:1 to ensure uniform filling of 0.3 mm thin-wall structures.
-
Surgical Knife Handle Molds: Utilize slider/lifter ejection mechanisms to achieve integrated molding of metal blades and plastic handles.
-
Multi-Cavity Mold Design: CAE software optimizes cavity pressure differences (≤5 MPa), enabling simultaneous production of 8 blood cell analyzer components per mold cycle.
Technological Breakthroughs:
-
Material Selection: Mold steel uses S136 stainless steel or SKD61 (hardness HRC 50-55 after nitriding), with hard chrome or diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings applied for 3x wear resistance.
-
Precision Control: Five-axis machining centers achieve positioning accuracy of ±0.001 mm, complemented by coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) and CT scanning for calibration.
-
Cleanliness Adaptation: Mold cavities must pass helium leak testing (leak rate ≤1 × 10⁻⁹ Pa·m³/s) and undergo ultrasonic cleaning every 5,000 mold cycles.

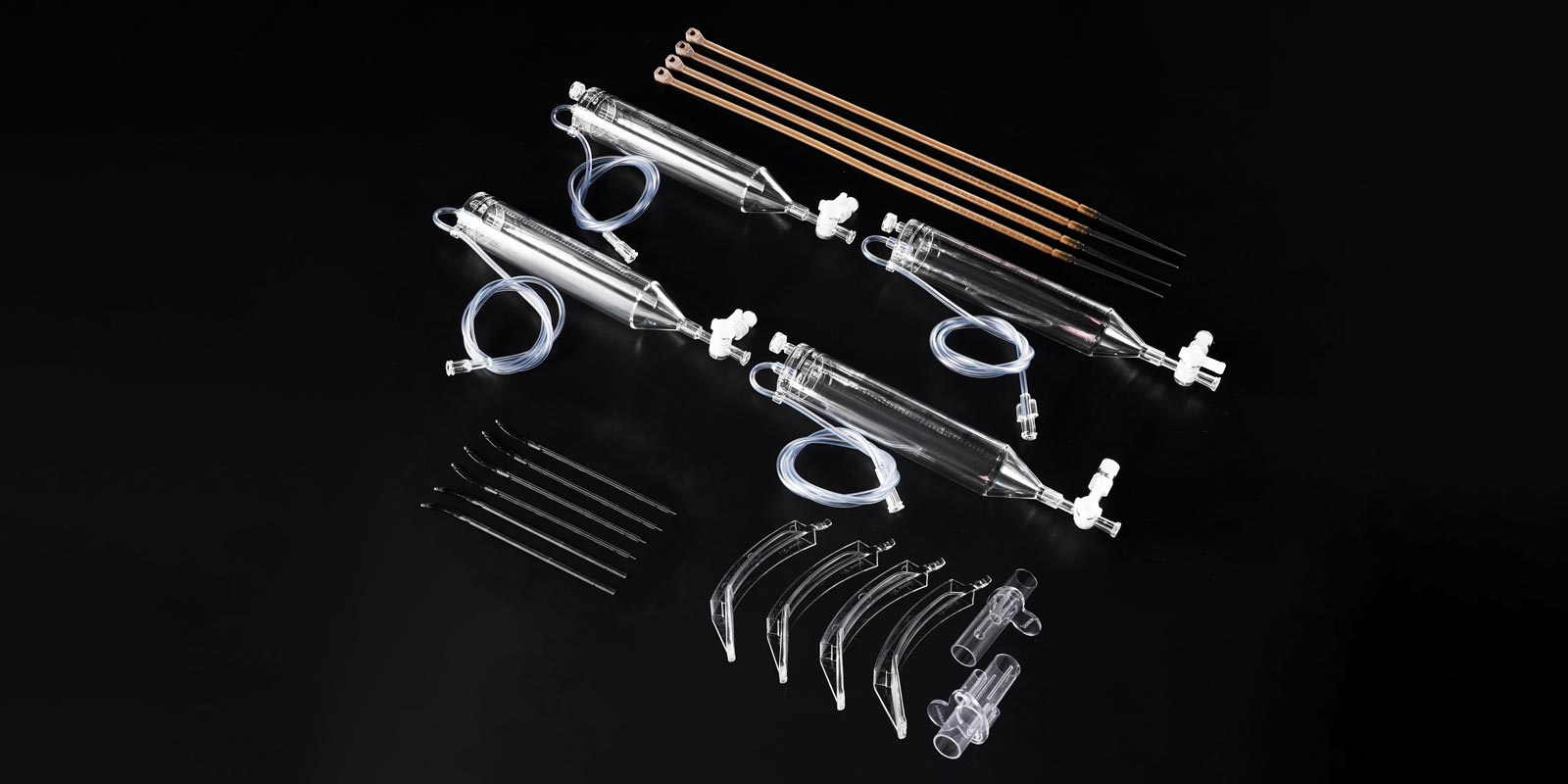
III. Injection Molding: Precision Manufacturing Under Closed-Loop Control
Taking a KraussMaffei all-electric injection molding machine as an example, its key process parameters are controlled as follows:
Innovative Processes:
-
Gas-Assisted Injection Molding: In the production of catheter ablation tools, nitrogen channels apply pressure to eliminate sink marks and reduce weight by 20%.
-
Insert Molding: Pre-placing stainless steel needles in the mold enables integrated molding of puncture needles, reducing assembly steps by 40%.
-
Two-Shot Molding: Overmolding TPE soft rubber onto ultrasound probe housings enhances grip comfort and slip resistance.
IV. Quality Inspection: Full-Process Traceability and Compliance Verification
Medical injection-molded parts undergo a three-tier inspection system:
-
First-Article Inspection: A coordinate measuring machine (CMM) checks critical dimensions (tolerance ±0.01 mm) with 100% coverage of geometric tolerances.
-
Online Inspection: High-speed vision systems capture 2,000 frames per second to detect defects such as 0.1 mm² weld lines and air pockets.
-
Final Inspection:
-
Physical Property Testing: Tensile strength, flexural modulus, and impact toughness must meet ASTM standards.
-
Biological Safety Testing: Passes 12 tests including cytotoxicity (MTT assay) and sensitization (skin patch test).
-
Sterilization Validation: After ethylene oxide, gamma radiation, or moist heat sterilization, the sterility assurance level (SAL) must reach 10⁻⁶.
Traceability System: Each component is marked with a production batch, mold number, operator information, etc., via laser marking or QR codes. Data is uploaded in real-time to a manufacturing execution system (MES), creating an electronic archive with 150 parameters to comply with FDA 21 CFR Part 11.
V. Industry Trends: The Integration of Intelligence and Green Manufacturing
-
AI Optimization: Machine learning analyzes historical production data to automatically adjust injection speed, holding time, and other parameters, reducing defect rates from 0.5% to 0.1%.
-
Digital Twin: Virtual simulation of the injection molding process predicts issues like warping and short shots in advance, shortening mold development cycles by 30%.
-
Sustainable Materials: The promotion of bio-based polycarbonates and biodegradable PLA reduces the environmental impact of medical waste.
The precision and intelligence of medical injection molding not only drive breakthroughs in the localization of high-end medical devices such as cardiac stents and artificial joints but also provide safe and reliable medical solutions for patients worldwide through a comprehensive quality control system. As material science and digital technologies continue to integrate, this traditional process is taking on a new vitality.














 Home
Home
